GPT-OSS: From Closed to Open: The New Family of LLMs from OpenAI

What is GPT-OSS?
Finally OpenAI shocked the world with the new open source models gpt-oss. gpt-oss is a new family of large language models released by OpenAI. It marks a significant shift for the organization, as these are the first open-weight models they’ve released since GPT-2. The family includes two models: gpt-oss-120b, a powerful 120 billion parameter model and a smaller gpt-oss-20b, 21 billion parameter model. These models are designed to be highly capable in reasoning tasks, adaptable for various applications, and efficient enough to run on consumer grade hardware. They are available under the permissive Apache 2.0 license, allowing for broad use and modification.
Key Features
- Gain complete access to the model’s reasoning process, facilitating easier debugging and increased trust in outputs.
- Supports a large context window of 128,000 tokens
- Easily adjust the reasoning effort to low, medium or high based on your specific use case.
- Fully customize models to your specific use case through parameter fine-tuning.
- Built-in support for tool use and function calling.
- Can be run on consumer-grade hardware.
How Does GPT-OSS Work?
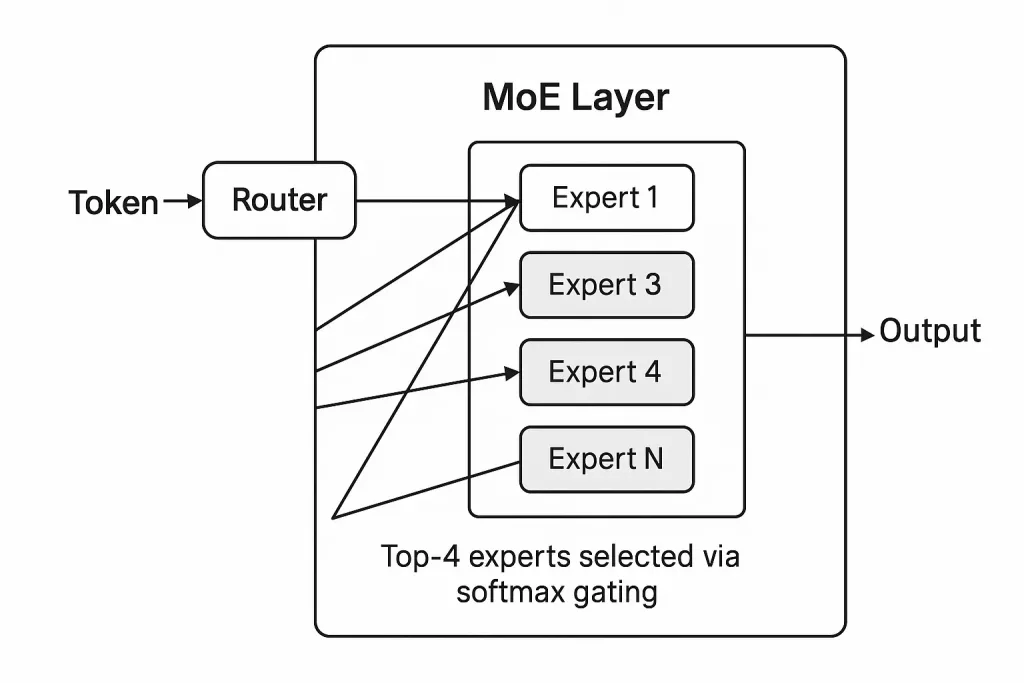
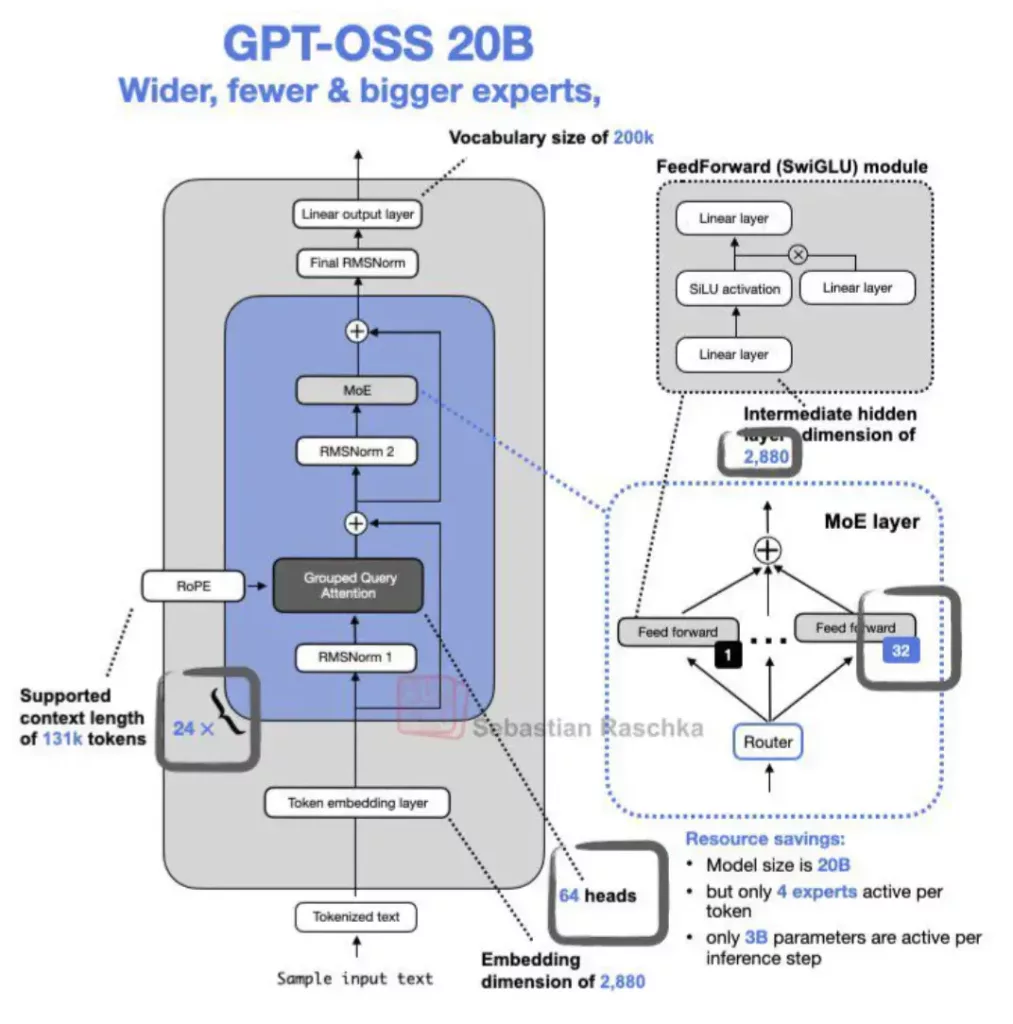
The GPT-OSS models are built on a Transformer architecture but with a key innovation: they are Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models. This means that while the models are very large overall, only a fraction of their parameters are activated for any given task. The 120B model has 128 experts per layer but only activates 4 of them at a time, resulting in only 5.1 billion active parameters. Similarly, the 20B model has 32 experts and activates 4, resulting in 3.6 billion active parameters. This sparse architecture, combined with techniques like grouped multi-query attention and native MXFP4 quantization, makes these models remarkably efficient to run.
Both models were trained on a dataset rich in STEM, coding, and general knowledge, and they use a new tokenizer called ‘o200k_harmony’ which is also open sourced. A crucial part of their training was a post training alignment phase, similar to the process used for GPT-4. This ensures they are good at following instructions and can perform complex reasoning tasks.
What Makes GPT-OSS Stand Out? Why Should You Use It?
The main attraction of gpt-oss is that it brings high end AI capabilities to the open-source community. For developers and researchers, this means they can now experiment with, fine-tune, and deploy models that are comparable in performance to some of OpenAI’s own proprietary models, like o4-mini, without the associated costs of using an API. It has a context window of 128,000 tokens, which is significantly larger than many existing models, and a unique “chain-of-thought” (CoT) system that provides transparency into the model’s reasoning process and you can set its reasoning level. Additionally, the models are designed for tool use and can interact with external APIs! See the benchmark for how well the gpt-oss-20B does with tools compared to models like o3.
Key Performance Benefits
GPT-OSS models show impressive performance on various benchmarks. The larger 120B model is said to be on par with or even exceed the performance of OpenAI’s internal o4-mini model in areas like coding (Codeforces), general problem-solving (MMLU and HLE), and tool use (TauBench). It has also shown strong results on specialized benchmarks like HealthBench, even outperforming some proprietary models. The smaller 20B model is also quite capable, matching or exceeding the performance of o3-mini on several benchmarks. You can see the benchmarks below.
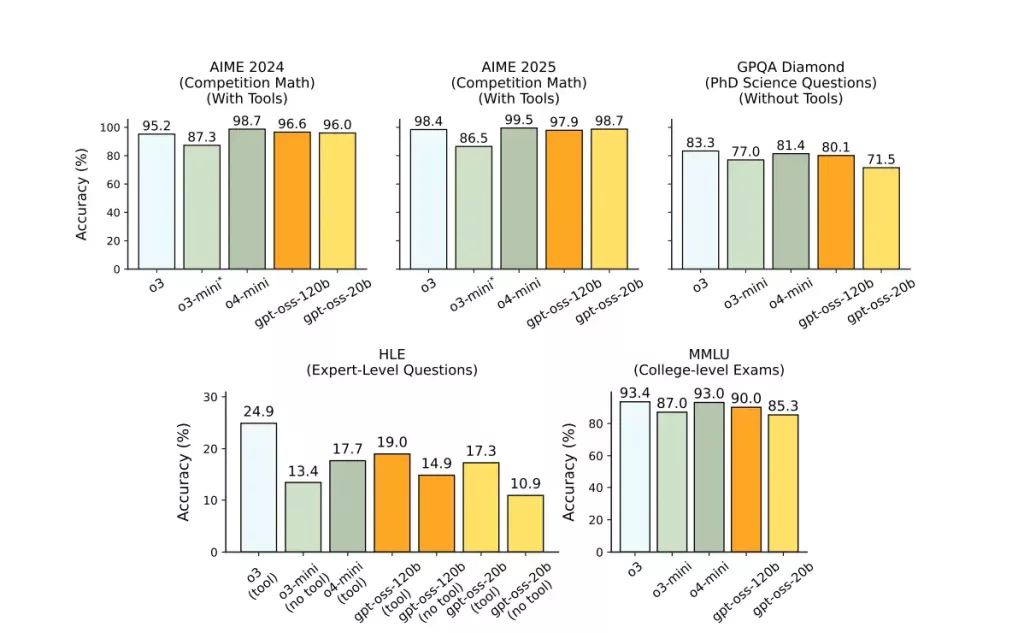
A key benefit is their efficiency. The 120B model can run on a single 80GB GPU like H100, and the 20B model can run on devices like your laptop with just 16GB of memory, which makes them accessible to a wider range of users.
Architecture Details
Both GPT-OSS models are based on the Transformer architecture. They utilize a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) approach to manage their large number of parameters efficiently. For example, the 120B model has 36 layers with 128 experts per layer, but only 4 experts are active for any given token, which helps to keep the computational cost down.
The models also use alternating dense and locally banded sparse attention patterns, a technique similar to the one used in GPT-3. For memory efficiency, they employ grouped multi-query attention with a group size of 8. Positional information is handled by Rotary Positional Embedding (RoPE), and the models natively support a context length of up to 128k tokens.
How to run GPT-OSS in Cordatus.ai ?
1. Connect to your device and select LLM Models from the sidebar.
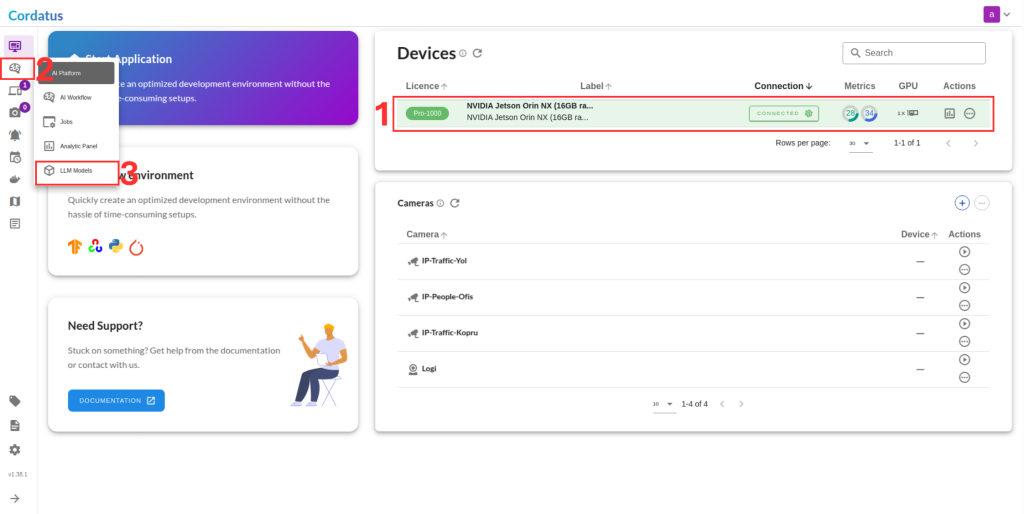
2. Select NIM from the model selector menu, choose your desired model, and click the Run symbol.
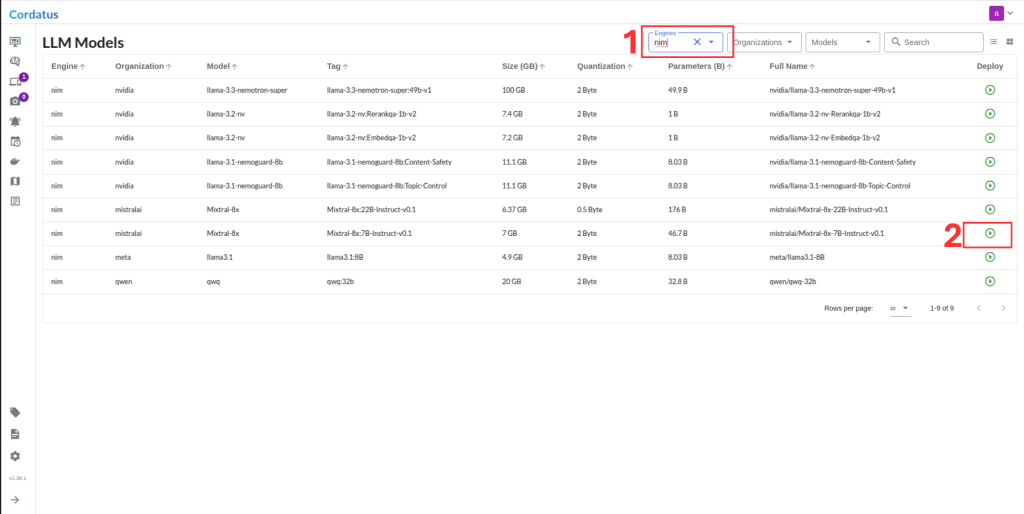
3. Click Run to start the deployment.
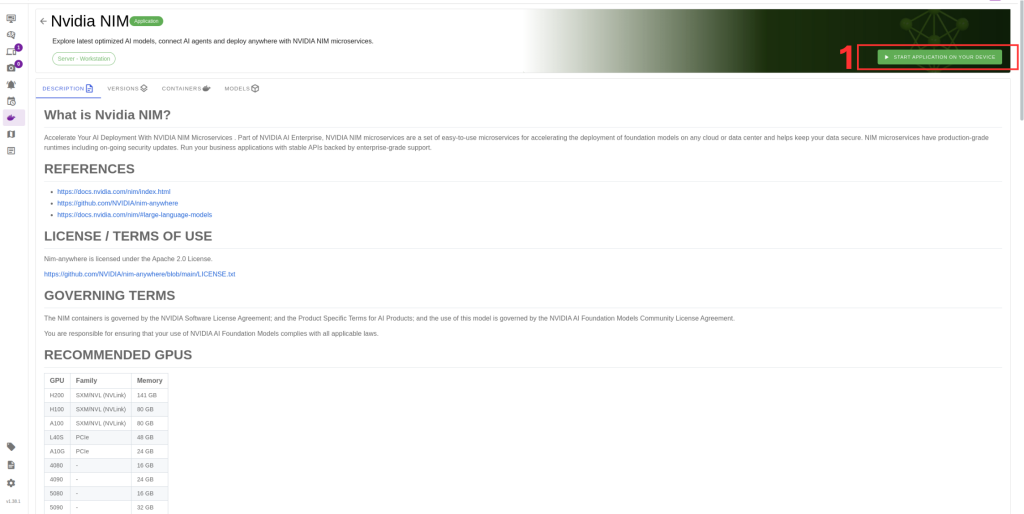
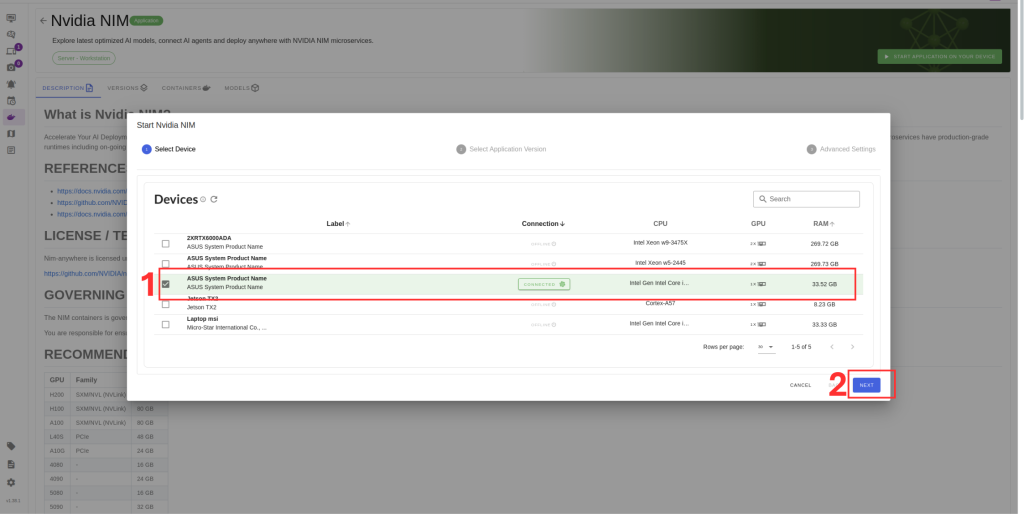
After selecting the model, follow these steps to complete the setup:
4. Select the target device where the LLM will run.
5. Choose the container version (if you have no idea select the latest).
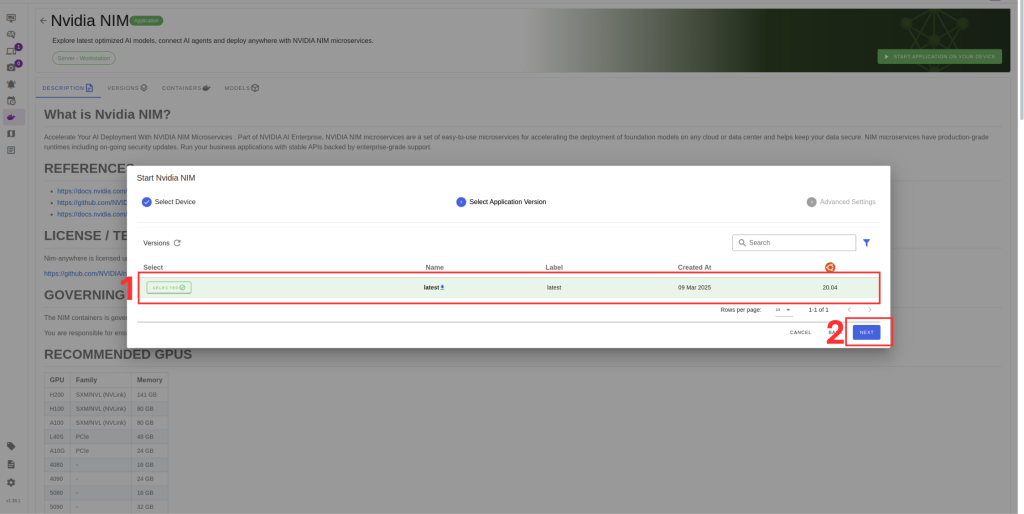
6. Verify the correct model is selected in Box 1.
7. If you have multiple GPUs you can select which ones you want to run LLM or you can select all GPUs option from Box 2.
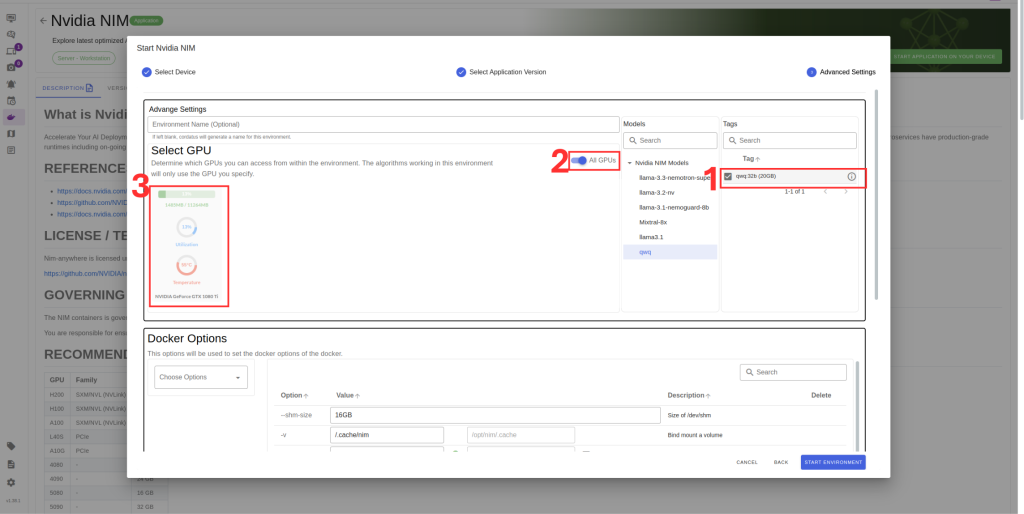
8. Check port availability in Box 3 .
9. Set NVIDIA token .You can obtain from build.nvidia.com.
10. You can setup Jupyter notebook if you desire.
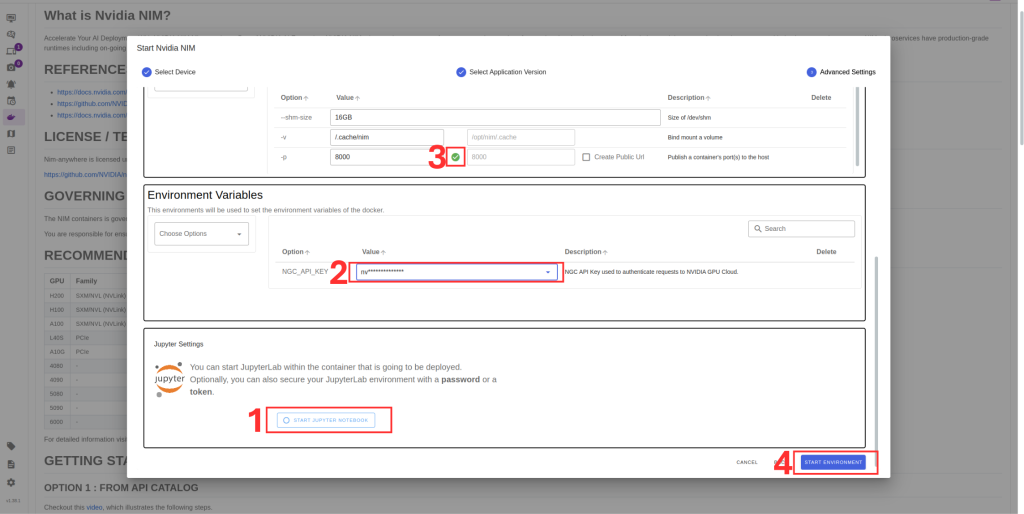
11. Click Save Environment to apply the settings.
Once these steps are completed, your model will start running automatically, and you can access it through the assigned port.